Publications
Preprint:
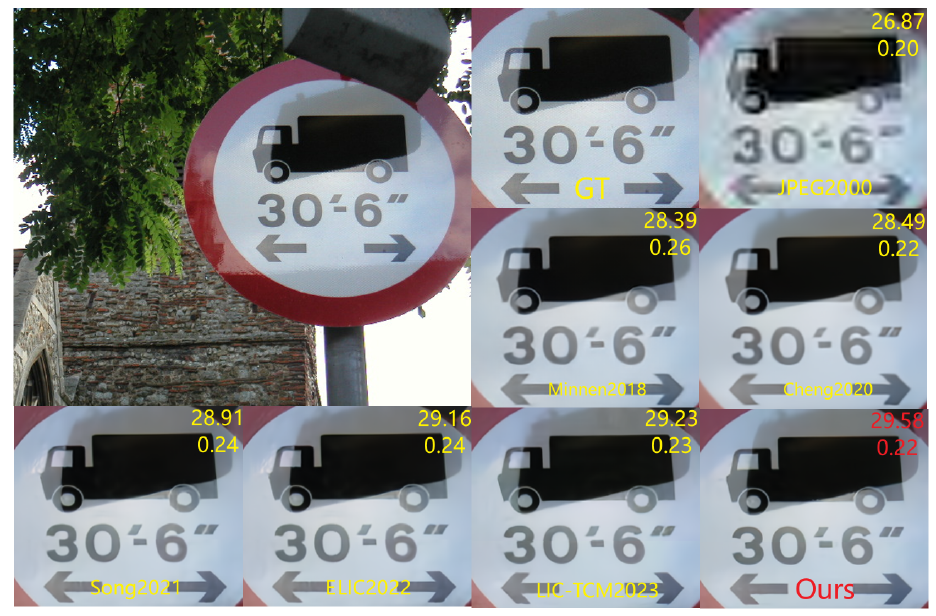

Abstract—In recent years, many task-oriented image compression methods have emerged. However, few have focused on maintaining and restoring text region information within image compression networks. Two key challenges arise when compressing scene text images: 1) guiding the compression network to prioritize text regions, and 2) minimizing distortion in text regions during lossy image compression. To address these challenges, we propose a learned image compression method that specifically targets text regions. We introduce a mask smoothing technique, which fine-tunes a text detection model to ensure seamless boundaries between text and background in reconstructed images. Additionally, the mask-guided transform (MGT) is designed to retain semantic information in text regions, reducing distortion during compression and ensuring better preservation of text features in the reconstructed images. At lower bit per pixel (bpp) rates, our method demonstrates superior performance in preserving text region quality compared to state-of- the-art methods, as validated on two benchmark datasets.

Abstract—In recent years, deep learning-based gaze estimation techniques using eye images have made significant progress. However, balancing prediction accuracy and computational complexity remains challenging. In this paper, we propose using the RAW data from a CMOS image sensor as the input, thereby avoiding the high computational demands of the traditional image signal processor (which converts RAW to RGB). We designed a special measuring scheme to collect and annotate a 12-bit RAW dataset. Additionally, we introduce the Multibit Attention Fusion Gaze Estimation Network (MAFN) to accurately perform gaze estimation using 12-bit RAW data. Our MAFN effectively extracts features of varying granularities through attention fusion techniques across different bit depths. We also employ Axial Sensitivity Spatial Attention, which is more sensitive to the horizontal and vertical position of the pupil in gaze angle prediction. Furthermore, we propose Bit Rolling Channelization and Neural Network-Friendly Quantization for lossless input of 12-bit data and low-bit data generation, respectively. Experimental results validate the effectiveness of MAFN and demonstrate the superiority of our method, showing that it can accurately measure gaze direction using 12-bit RAW data.
Accept:
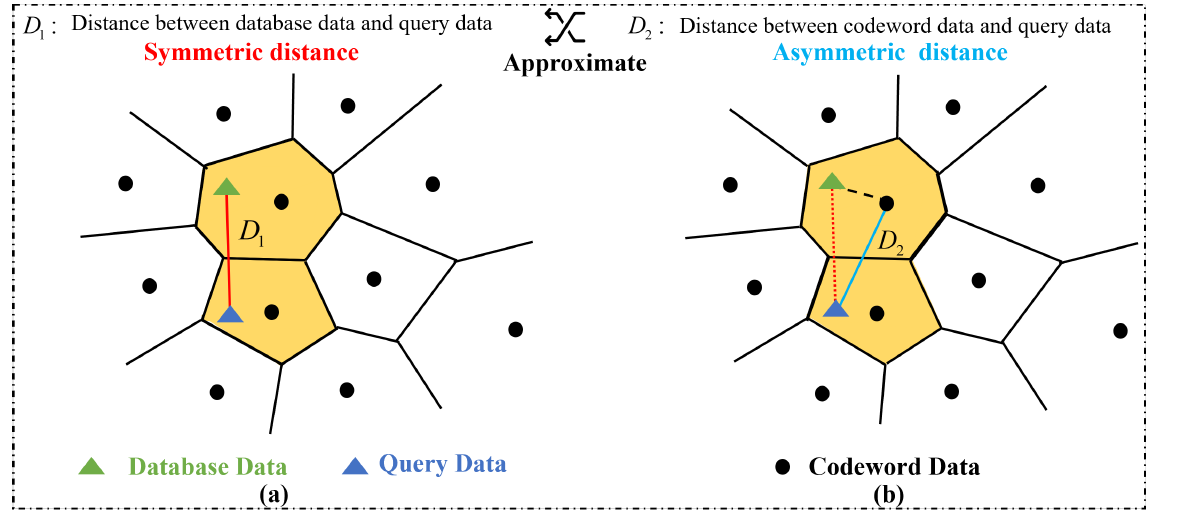
Data search plays a key role in information retrieval and machine learning. Currently, the Field Programmable Gate Array (FPGA) has emerged as a popular hardware accelerator for such studies. In order to maintain a better balance between search time and accuracy, we introduce FCCQA, an exhaustive and scalable data search architecture, utilizing Approximate Nearest Neighbor (ANN) for rapid interrogation of high-dimensional datasets on FPGA. Our architecture adopts the technique of compositing quantization to achieve a high data compression ratio, reducing memory usage to about 1.67%, while efficiently transforming the intricate computation into a simplified table lookup operation in high-dimensional datasets. Compared with GPU and CPU, our approach establishes a superior balance among accuracy, energy efficiency and speed.